XML Schema
XML DTD의 특징
- 장점
- 어플리케이션과 독립적으로 유효성 검증이 가능
- 속성에 대하여 값의 유형 제한이나 기본값 제공이 가능
- 문서의 모듈화 가능
- DTD의 제약점
- XML 문법과 다르다 : SGML 문법에 기초
- 데이터 형식에 대한 지원 부족 : 요소의 내용이 텍스트로 제한, 숫자 처리 불가능
- 내용 모델 기술에 한계 : 상속/객체지향 개념 불완전, 반복성 제어 한계 (예, "k번 반복" 불가능)
- XML 네임스페이스 지원이 불완전
XML Schema의 장점
- XML 문법을 사용한다. - DTD는 SGML 문법을 사용
- namespace를 완전히 지원한다. - DTD에서는 namespace 지원이 불완전
- data type 지원 - DTD에서는 구조와 텍스트 내용의 요소까지만 정의 가능
- Schema 에서는 <simpleType>에서 다양한 데이터 형식 가능
- content model 이 다양
- 재사용이 용이 : DTD에서는 파라메터 엔티티를 사용
- 다양한 구조 가능 : 반복 횟수, 선택적 요소 구성 등.
*** Schema에는 ENTITY 기능이 없다 => DTD가 계속 사용될 이유...
XML Schema 소개
- History
- 1999 요구사항 초안 (requirement specification)
- 2001.3 XML Schema 1.0 published
- 2002.11 XML Schema 1.1 requirement specification
- 사용
- Schema Validator
- XML Schema 유효성 검사 기능을 포함한 파서: MSXML4, Xerces Java Parser 등
- XML Schema 파일
- 외부 DTD와 같은 역할
- XML Schema의 인스턴스 문서
- Schema Validator
DTD와 XML Schema 비교
- 예제 DTD 및 문서
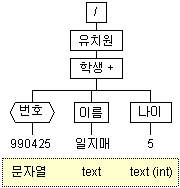
<!ELEMENT 유치원 (학생+)>
<!ELEMENT 학생 (이름, 나이)>
<!ATTLIST 학생 번호 CDATA #REQUIRED>
<!ELEMENT 이름 (#PCDATA)>
<!ELEMENT 나이 (#PCDATA)><!DOCTYPE 유치원 SYSTEM "ex07.dtd">
<유치원>
<학생 번호="990425">
<이름>일지매</이름>
<나이>5</나이>
</학생>
</유치원>
- Microsoft Schema
- 사용하지 말 것 -일부 문법이 다르다
- Shema11-01.xml (일부수정)
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="EUC-KR"?>
<Schema xmlns="urn:schemas-microsoft-com:xml-data" xmlns:dt="urn:schemas-microsoft-com:datatypes">
<AttributeType name='번호' dt:type='string' required='yes'/>
<ElementType name='이름' content='textOnly'/>
<ElementType name='나이' content='textOnly' dt:type='int'/>
<ElementType name='학생' content='mixed'>
<attribute type='번호'/>
<element type='이름'/>
<element type='나이'/>
</ElementType>
<ElementType name='유치원' content='eltOnly'>
<element type='학생'/>
</ElementType>
</Schema>- s11-01.xml (일부수정)
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="EUC-KR"?>
<유치원 xmlns="my-schema:Shema11-01.xml">
<학생 번호="990425">
<이름>일지매</이름>
<나이>5</나이>
</학생>
</유치원>
- W3C XML Schema
- Shema12-01.xml (일부수정)
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="EUC-KR"?> 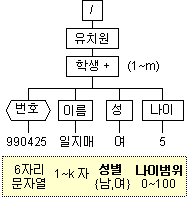
<schema xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema">
<simpleType name="나이범위" base="integer">
<minInclusive value="0" />
<maxInclusive value="100" />
</simpleType>
<simpleType name ="성별" base="string">
<enumeration value="남" />
<enumeration value="여" />
</simpleType>
<element name ="유치원">
<complexType content="elementOnly">
<element name ="학생">
<complexType content="mixed">
<attribute name ="번호" type="string" />
<element name="이름" type='textOnly'/>
<element name='성' type='성별'/>
<element name='나이' type='나이범위' />
</complexType>
</element>
</complexType>
</element>
</schema>- s12-01.xml (일부수정)
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="EUC-KR"?>
<유치원 xmlns="my-schema:Shema12-01.xml">
<학생 번호="990425">
<이름>일지매</이름>
<성>여</성>
<나이>5</나이>
</학생>
</유치원>
XML Schema 기초
- 루트 요소 선언 <schema>
- <schema xmlns="URI"
targetNamespace="URI" ... >
- Schema namespace 접두사 사용시
- 예)
<xs:schema xmlns:xs="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema" ...>
<xs:element name="성명">
<xs:complexType>
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element name="이름" type="xs:string"/> ...
- 예)
- <schema xmlns="URI"
- 요소의 정의 <element>, <group>, <attribute>, <attributeGroup>
<element name="요소 이름" type="요소 형식" ref="전역요소 참조"
minOccurs="음아닌 정수" maxOccurs="음아닌 정수 | unbound" ...>
- 내장 데이터 형식
- primitive data types
- string, boolean, decimal, float, double, ...
- duration, dateTime, time, date, ... ,
- hexBinary, base64Binary, any URI, QName, NOTATION
- derived types
- normalizedString, integer, positiveInteger,
- nonPositiveInteger, negativeInteger, nonNegativeInteger,
- long, int, short, byte, unsignedLong, unsignedShort, unsignedByte, ...
- primitive data types
- 사용자 정의 데이터 형식
- <simpleType>, <restriction>, <list>, <union>
- 내용 모델 (구조 모델)
- <complexType>, <sequence>, <choice>
시작 예제
- 예제) name5.xsd
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="EUC-KR"?>
<schema xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema"
targetNamespace="http://mm.sookmyung.ac.kr/names"
xmlns:target="http://mm.sookmyung.ac.kr/names" >
<element name="성명">
<complexType>
<sequence>
<element name="이름" type="string"/>
<element name="별명" type="string"/>
<element name="성" type="string"/>
</sequence>
<attribute name="호칭" type="string"/>
</complexType>
</element>
</schema>- name5.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="EUC-KR"?>
<성명 호칭="Mr."
xmlns="http://mm.sookmyung.ac.kr/names"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://mm.sookmyung.ac.kr/names name1.xsd" >
<이름>길동</이름>
<별명>장군</별명>
<성>홍</성>
</성명>
사용자 정의 데이터 형식 : <simpleType>
- <simpleType name="이름" ...>
- 다른 데이터 형식에서 유도하여 simpleType의 데이터 형식을 지정 (derived type)
- <restriction>, <list>, <union>
- <restriction base="유도되는 기초형식의 simpleType 이름">
... 제한 Facet 설정 ...
</restriction>
- base type의 부분 집합을 지정하기 위하여 facet 설정 : 값 또는 범위 등을 제한
- 12가지의 restriction facet
- minExclusive, maxExclusive, minInclusive, maxInclusive,
- totalDigits, fractionDigits, length, minLength, maxLength,
- enumeration, whitespace, pattern
- 예)
<성명 호칭="Dr."> ..
<성명 호칭="Mr."> ...
호칭을 몇가지 주어진 단어로 제한.
예) Mr. Ms. Dr. Princess, ...<attribute name="호칭"/>
<simpleType>
<restriction base="string">
<enumeration value="Mr."/>
<enumeration value="Ms."/>
<enumeration value="Dr."/>
<enumeration value="Princess"/>
</restriction>
</simpleType>
</attribute><분>25</분>
<분>6</분>
<분>0</분>
오류 : <분>-5</분>
오류 : <분>60</분><element name="분"/>
<simpleType>
<restriction base="nonNegativeInteger">
<maxExclusive value="60"/>
</restriction>
</simpleType>
</element>
- <list itemType="항목의 형식 simpleType의 이름">
- 하나의 요소 내에 여러개를 나열하고 싶을 때
- 예)
<번호목록>0 26 21 9</번호목록>
<번호목록>61</번호목록><element name="번호목록"/>
<simpleType>
<list itemType="nonNegativeInteger"/>
</simpleType>
</element><성씨>홍 김 임 황보</성씨>
<성씨>최 안 이 차 설 김 유 이 김 조 이 박 이</성씨><element name="성씨"/>
<simpleType>
<list itemType="string"/>
</simpleType>
</element>
- <union memberTypes="형식의 리스트"/>
- 여러 개의 형식을 결합시켜서, 하나의 요소내에서 사용할 때
- 예)
<Nations>Korea</Nations>
<Nations>Japan</Nations>
<국가명>대한민국</국가명>
<국가명>독일</국가명><simpleType name="Nations">
<restriction base="string">
<enumeration value="Korea"/>
<enumeration value="Japan"/>
<enumeration value="USA"/>
</restriction>
</simpleType>
<simpleType name="국가명">
<restriction base="string">
<enumeration value="대한민국"/>
<enumeration value="독일"/>
<enumeration value="브라질"/>
</restriction>
</simpleType><나라>Korea</나라>
<나라>대한민국</나라>
<나라>USA</나라>
<나라>브라질</나라><element name="나라"/>
<simpleType>
<union membertype="Nations 국가명"/>
</simpleType>
</element>- 동시에 사용은 못한다 : 합집합 개념
- 예) <나라>Korea 대한민국</나라> : X
내용 모델 <complexType>
- <complexType name="이름" mixed="true | false" >
<sequence>, <choice>, <all>등을 이용하여 모델의 구조를 선언하고,
해당하는 요소 또는 속성을 나열
</complexType>- 전역 형식에는 name 속성이 있고, 지역 형식에는 이름이 없어야 한다
- <sequence minOccurs="..." maxOccurs="..." >
- 순차구조, 여러번 반복하려면 cardinality 이용
- 내부에 <element>, <choice>, <group> 참조 등 포함 가능
<성명>
<이름>길동</이름>
<별명>장군</별명>
<성>홍</성>
</성명><element name="성명">
<complexType>
<sequence>
<element name="이름" type="string"/>
<element name="별명" type="string"/>
<element name="성" type="string"/>
</sequence>
</complexType>
</element>오류: <성명>
<성>홍</성>
<이름>길동</이름>
<별명>장군</별명>
</성명><성명>
<별명>장군</별명>
<성>홍</성>
<이름>길동</이름>
</성명><성명>
<성>홍</성>
<이름>길동</이름>
</성명>
- <choice minOccurs="..." maxOccurs="..." >
- 선택구조, 내용중 한가지만 선택 가능
- 여러개 선택하려면 cardinality 이용
<출석부>
<이름>길동</이름>
<이름>남일</이름>
<별명>공주</별명>
<이름>싸이</이름>
<별명>테리우스</별명>
<성>일</성>
</출석부><element name="출석부">
<complexType>
<choice minOccurs=1 maxOccurs=60 >
<element name="이름" type="string"/>
<element name="별명" type="string"/>
<element name="성" type="string"/>
</choice>
</complexType>
</element><p>내일 <b>오전</b>에 중요한 <b>회의</b>가 있으니, <i>반드시</i> 참석하시기 바랍니다.</p> <element name="p" >
<complexType mixed="true">
<choice minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="unbound">
<element name="b" type="string">
<element name="i" type="string">
</choice>
</complexType>
</element>
- <all minOccurs="0 또는 1" maxOccurs="0 또는 1" >
- 순서와 상관없이 요소 사용, 단, 최대 1번만 가능
- 반드시 <complexType>의 자식으로 선언
- 예
<성명>
<이름>길동</이름>
<별명>장군</별명>
<성>홍</성>
</성명>
<성명>
<별명>장군</별명>
<성>홍</성>
<이름>길동</이름>
</성명><element name="성명">
<complexType>
<all>
<element name="이름" type="string"/>
<element name="별명" type="string"/>
<element name="성" type="string"/>
</all>
</complexType>
</element>
요소의 정의 <element>, <any>, <group>
<element name="요소 이름" type="(전역)요소 형식" ref="전역요소 참조"
minOccurs="음아닌 정수" maxOccurs="음아닌 정수 | unbound"
default="기본 값" fixed="고정 값">
- 전역선언(global declaration)과 지역선언(local declaration)
- 요소정의 방법- 지역에서 선언 (사용)
- 전역형식을 정의하고 요소에서 형식을 사용
- 정의된 요소를 (전역요소) 다른 요소에서 참조
- 지역선언
- 정의된 컨텐츠 내에서만 사용
- <element>내에서 <complexType> 또는 <simpleType>으로 선언
<element name="성명">
<complexType>
... 형식 정보 ...
</complexType>
</element><element name="성명">
<simpleType>
... 형식 정보 ...
</simpleType>
</element>
- 전역형식의 정의 및 사용
- <schema>의 자식요소, Schema 문서에서 재사용가능
- <complexType> 또는 <simpleType>으로 전역형식을 선언하고,
<element name="..." type="전역형식"> 정의에서 사용
<schema xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema" ...>
<complexType name="이름정의">
<sequence>
<element name="이름" type="string"/>
<element name="성" type="string"/>
</sequence>
</complexType>
...
<element name="성명" type="이름정의"/>
</schema>
전역형식(type) 선언
=> 재사용 가능
전역형식 사용 - string
=> Schema에서 선언
전역형식 사용 - 이름정의
=> 문서 내에서 선언
- 기존의 전역요소를 참조
- <element name="요소A">으로 정의된 요소를
다른요소 <element ref="요소A">에서 참조
<schema ... >
<element name="이름" type="string"/>
<element name="성" type="string"/>
...
<complexType name="이름정의">
<sequence>
<element ref="이름" />
<element ref="성" />
</sequence>
</complexType>
...
<element name="성명" type="이름정의"/>
</schema>
전역요소 선언 - 이름, 성
전역형식(type) 선언
- 이름정의
전역요소 사용 - 이름, 성
=> 문서 내에서 선언
전역형식 사용 - 이름정의
=> 문서 내에서 선언 - <element name="요소A">으로 정의된 요소를
- cardinality :
- minOccurs="음아닌 정수" maxOccurs="음아닌 정수 | unbound"
- 전역 요소에서는 사용 불가
- 예
<element name="학생" type="명단" minOccurs="10" maxOccurs="60">
<element name="이름" type="string" minOccurs="1" maxOccurs="1">
<element name="별명1" type="string" minOccurs="1" maxOccurs="3">
<element ref="별명2" maxOccurs="10"> <!-- overriding -->
<element name="별명3" type="string" minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="unbound">
- 요소 와일드카드 : 생략 <any minOccurs="..." maxOccurs="..." ...>
- 전역 그룹 선언
- <group name="전역 그룹 이름" >
- 예
<group name="이름그룹">
<sequence>
<element name="이름" type="string"/>
<element name="별명" type="string"/>
<element name="성" type="string"/>
</sequence>
</group>
...
<element name="성명" >
<complexType>
<group ref="이름그룹" />
</complexType>
</element>
전역 그룹 선언
- mm:이름그룹
전역그룹 사용
=> mm 문서 내에서 선언
속성의 선언 <attribute>, <attributeGroup>
<attribute name="속성 이름" type="전역 형식" ref="전역속성 참조"
use="optional | prohibited | required" default="기본 값" fixed="고정 값">
- 속성의 형식 선언 방법
- 지역형식 사용 : <simpleType>으로 선언만 가능
- <attribute name="호칭">
<simpleType>
... 형식 정보 ...
</simpleType>
</attribute>
- <attribute name="호칭">
- 전역형식 사용 : type="전역형식" 속성 사용
- <attribute name="호칭" type="string"/>
- <attribute name="호칭" type="string"/>
- 기존 전역속성의 참조 : ref="전역속성" 속성 사용
- 반드시 접두사 사용, 다른 지역 형식 포함 불가능
- 예 : <attribute ref="mm:호칭"/>
- 지역형식 사용 : <simpleType>으로 선언만 가능
- use 속성 : 사용 방법
- required : 반드시
- optional : 필요시
- prohibited : 사용 금지 - 예) wildcard로 정의시, 그룹 참조시
- 속성 와일드카드 : 생략 <anyAttribute namespace="..." processContents="..." />
- 속성 그룹 선언 : 생략 <attributeGroup name="전역속성 그룹 이름" >
[출처] XML Schema |작성자 아는남자
'웹지능화서비스' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 대용량 데이터 처리를 위한 RDB 기반 온톨로지 모델링 및 구축사례 (0) | 2008.05.16 |
|---|---|
| ETRI, 시맨틱 웹 추론엔진 개발 (0) | 2008.05.16 |
| ETRI 추론 엔진 '보쌈(bossam)' (0) | 2008.05.16 |
| ETRI, ‘똑똑한 로봇’ 가능한 추론엔진 ‘보쌈’ 첫 개발 (0) | 2008.05.16 |
| 온톨로지(Ontology) (0) | 2008.05.16 |
댓글